From Tiny Mice to Giant Capybaras: Understanding the Scale of Earth’s Largest Rodent
The capybara, also known as Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, is the largest living rodent in the world. Native to South America, these semi-aquatic mammals are found in a variety of habitats, including rivers, lakes, and marshes. Capybaras are known for their social nature and can often be found in groups of 10 to 20 individuals, although larger groups have been observed.
They are herbivorous animals, feeding on a diet of grasses and aquatic plants. Capybaras are also excellent swimmers and can stay submerged for up to five minutes at a time. Due to their unique characteristics and behaviors, capybaras have become a popular subject of fascination for animal enthusiasts around the world.

Size and Physical Characteristics of the Capybara
Capybaras are large, robust animals with a barrel-shaped body and short, sturdy legs. They have a head and body length of around 3.5 to 4.5 feet and can weigh anywhere from 77 to 146 pounds, with males typically being larger than females. Their fur is coarse and varies in color from reddish-brown to gray, with a lighter underbelly.
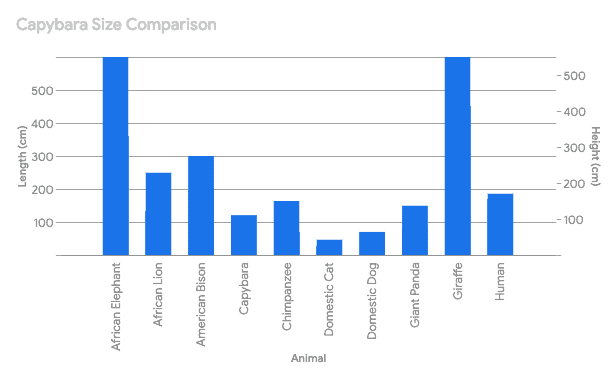
Here’s a table comparing the capybara’s size to 10 popular animals, with some extra details to make it more informative:
| Animal | Scientific Name | Average Weight (kg) | Average Length (cm) | Height (cm) | Comparison to Capybara |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capybara | Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris | 50 | 120 | 60 | – |
| Domestic Cat | Felis catus | 4.5 | 46 | 25 | Much smaller and lighter, about 1/10th the weight. |
| Domestic Dog | Canis familiaris | Varies greatly (5-90) | Varies greatly (30-100) | Varies greatly | Can be smaller or larger depending on breed. A large dog breed like a Great Dane can outweigh a capybara. |
| Human | Homo sapiens | 70 | 170 | 170 | Taller and heavier, but similar in length. |
| Chimpanzee | Pan troglodytes | 52 | 70 (standing) | 150 | Lighter and shorter, but similar height when standing. |
| Giant Panda | Ailuropoda melanoleuca | 100 | 150 | 75 | Heavier, but shorter in length and height. |
| African Lion | Panthera leo | 190 | 250 | 120 | Much heavier and longer, almost twice the size. |
| American Bison | Bison bison | 725 | 300 | 180 | Significantly heavier and taller, over 14 times the weight. |
| African Elephant | Loxodonta africana | 6000 | 600 | 330 | Immensely larger and heavier, over 100 times the weight. |
| Giraffe | Giraffa camelopardalis | 1600 | 450 | 550 | Much taller and heavier, and significantly longer. |
Capybaras have webbed feet, which make them excellent swimmers, and their eyes, ears, and nostrils are located on top of their head, allowing them to keep most of their body submerged while still being able to see, hear, and breathe.
Their teeth are constantly growing, which is a common trait among rodents, and they use them to graze on grasses and aquatic plants. Overall, capybaras have a unique and distinctive appearance that sets them apart from other rodents.
Capybara vs. Other Large Rodents

Capybaras are often compared to other large rodents, such as beavers and nutrias, but they have several distinct differences that set them apart. While beavers are known for their large, flat tails and semi-aquatic lifestyle, capybaras have a more streamlined body and are fully adapted to an aquatic environment. Nutrias, on the other hand, are smaller than capybaras and have a more rat-like appearance, with long tails and sharp incisors.
| Feature | Capybara ( Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris ) | North American Beaver (Castor canadensis) | Coypu (Myocastor coypus) | Marmot (various species) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Up to 1.3m long, 60kg | Up to 1.2m long, 32kg | Up to 60cm long, 10kg | Up to 76cm long, 13kg |
| Weight | Heaviest living rodent | 2nd heaviest living rodent | ||
| Build | Barrel-shaped, short legs | Stocky, powerful tail | Rat-like, long tail | Stout, short limbs |
| Habitat | Wetlands, near water | Rivers, streams, builds dams | Near water, good burrower | Grasslands, mountains |
| Social | Highly social, large groups | Family groups, territorial | Solitary or small groups | Varies by species |
| Diet | Primarily grasses, aquatic plants | Tree bark, aquatic plants | Aquatic plants, shellfish | Plants, insects |
| Unique Trait | Partially webbed feet | Large, flat tail for swimming, building | Orange-yellow teeth | Hibernation in winter |
Capybaras are also more social than these other rodents, often forming large groups and engaging in communal activities such as grooming and vocal communication. Additionally, capybaras have a more herbivorous diet compared to beavers, which are known for their ability to construct dams and feed on a variety of plant and animal matter.
Capybara Habitat and Behavior

Capybaras are found in a variety of habitats throughout South America, including savannas, rainforests, and wetlands. They are highly adaptable animals and can thrive in both freshwater and saltwater environments. Capybaras are social creatures and are often found in groups of 10 to 20 individuals, although larger groups have been observed in some areas.
They communicate through vocalizations such as barks, whistles, and purrs, as well as through scent marking using their anal glands. Capybaras are also excellent swimmers and spend a significant amount of time in the water, where they can stay submerged for up to five minutes at a time.
They are primarily herbivorous animals, feeding on a diet of grasses and aquatic plants, although they have been known to occasionally consume fruits and vegetables as well.
Capybara as a Popular Pet
In recent years, capybaras have gained popularity as exotic pets in some parts of the world. Their docile nature and social behavior make them appealing to some animal enthusiasts, although they require a significant amount of space and access to water in order to thrive.
Capybaras are legal to own as pets in some countries, such as the United States, although they require special permits and licenses due to their status as exotic animals.
However, owning a capybara as a pet is not without its challenges, as they require a specialized diet, veterinary care, and socialization with other capybaras in order to live a healthy and fulfilling life. Additionally, capybaras are highly social animals and require constant companionship in order to thrive, making them unsuitable for individuals who cannot provide them with the necessary care and attention.
Conservation Status of the Capybara
The conservation status of the capybara is currently listed as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This is due to their wide distribution throughout South America and their ability to adapt to a variety of habitats. However, capybaras face several threats to their survival, including habitat loss due to deforestation and agricultural expansion, as well as hunting for their meat and fur.
In some areas, capybaras are also considered agricultural pests and are targeted by farmers for crop damage. Efforts are being made to protect capybara populations through the establishment of protected areas and conservation programs, as well as through education and outreach efforts aimed at reducing human-wildlife conflict.

The Fascinating World of the Capybara
In conclusion, the capybara is a fascinating and unique animal that has captured the interest of animal enthusiasts around the world. From their large size and distinctive physical characteristics to their social behavior and adaptability to various habitats, capybaras are truly one-of-a-kind creatures. While they face several threats to their survival, efforts are being made to protect capybara populations and ensure their long-term survival in the wild.
As exotic pets, capybaras require specialized care and attention in order to thrive, making them unsuitable for all individuals. Overall, the capybara is an incredible animal that continues to captivate the imagination of people everywhere with its remarkable traits and behaviors.